Heat exchange systems are crucial components in a variety of industries, playing a key role in moving heat between two or more fluids. Their performance and functionality are not only essential to improving energy use but also essential for maintaining process safety and performance in multiple fields, from energy production to food manufacturing. Understanding what heat exchangers are and how they function is the initial step toward capitalizing on their benefits optimally.
In this article, we will examine the several types of heat exchangers, their functions, and how to select the right one for your specific needs. We will investigate the nuances of design factors, innovations in tech, and maintenance practices that can considerably boost the life span and efficiency of these systems. By linking between theory and practical application, we aim to provide a detailed guide for those seeking to tap into the capabilities of heat exchangers in their projects.
Comprehending Heat Exchangers
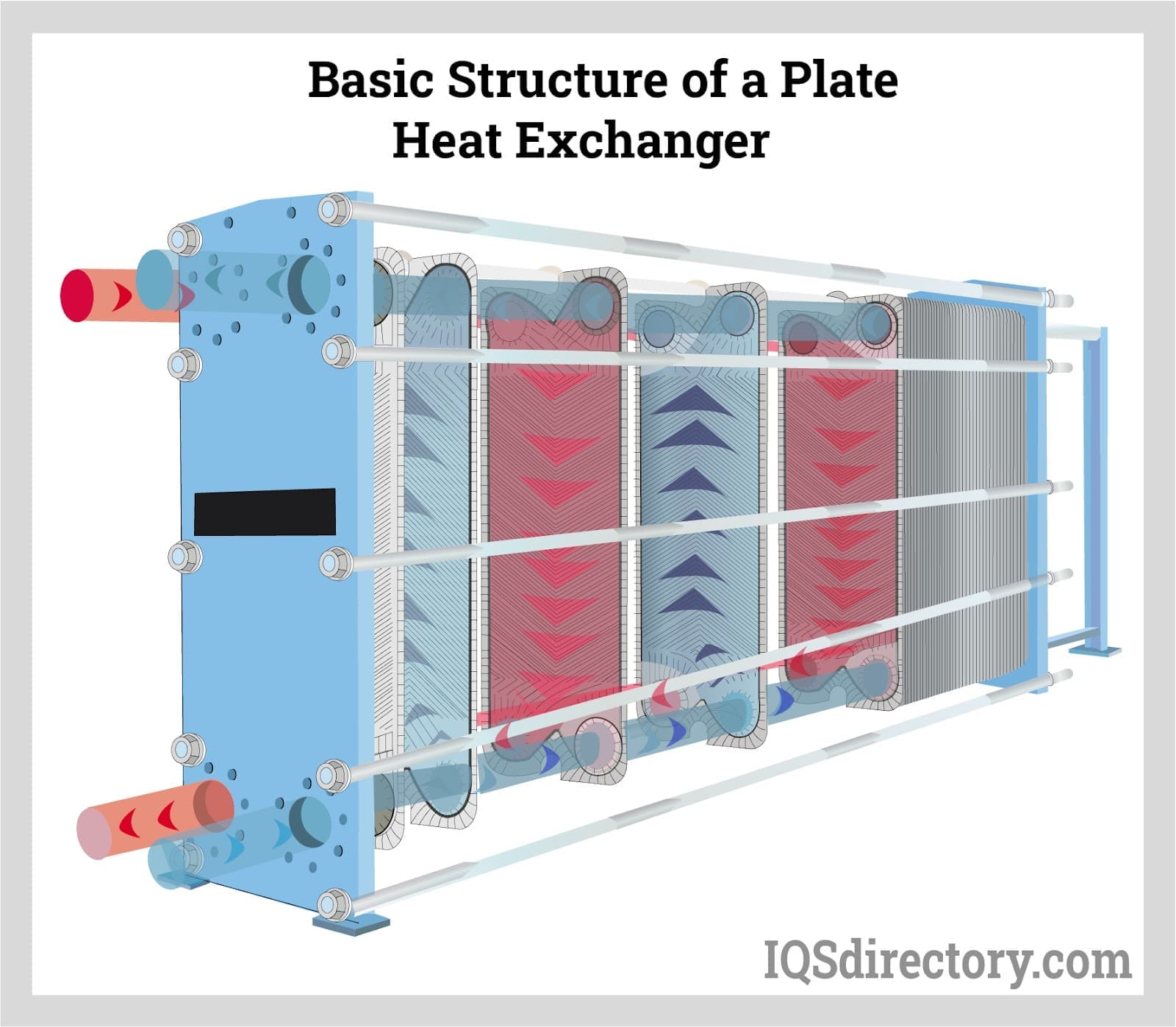
Heat exchange systems are crucial devices designed to conduct heat between two fluids without mixing them. They work on the concept of heat transfer, where thermal energy is moved from a hotter fluid to a cooler one, efficiently allowing temperature control in multiple settings. The basic mechanism often involves conductive heat transfer, which takes place through a separator that separates the fluids. This process plays a crucial role in improving energy efficiency and managing thermal processes throughout industries.
There are many different types of heat exchangers, each tailored for particular applications and operating conditions. Common configurations include shell-and-tube heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers, and air-cooled units. The selection of design often depends on factors such as heat transfer efficiency, space constraints, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for professionals who aim to select the suitable type for their particular project needs.
In addition to their fundamental function of heat transfer, heat exchangers significantly impact energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. By maximizing energy recovery and minimizing waste, they aid in reduced operational costs and diminished carbon emissions. Their role extends beyond just industrial applications, as they are integral components in HVAC systems, power plants, refrigeration, and even sustainable energy systems, highlighting their flexibility and importance in modern technology.
Uses and Advantages
Heat exchange devices play a key role in various industries, making them necessary in sectors such as oil and gas, the chemical industry, and energy production. In the oil and gas industry, heat exchangers are employed to efficiently transfer heat during refining operations, ensuring maximum efficiency and reduction in energy costs. Similarly, in Click for source manufacturing, these devices help maintain precise temperatures required for chemical reactions, thereby enhancing the quality of products and process efficiency. Their versatility allows for efficient heat recovery processes, minimizing waste and maximizing output in these critical industries.
The efficiency of energy provided by heat exchangers is a significant benefit that cannot be ignored. By recovering waste heat from industrial processes, these devices lower energy usage and lower operating costs. This efficiency is particularly clear in HVAC systems, where heat exchangers improve indoor air quality and comfort levels while reducing energy bills for business and homes. Additionally, their role in renewable energy systems, such as solar energy systems and geothermal solutions, highlights their role in fostering sustainability across sectors.
Cost savings are another significant advantage of utilizing heat exchangers. They not only reduce energy expenses but also cut maintenance and repair costs when well-designed and maintained. Innovations in heat exchanger design, such as compact solutions and the use of materials like high-quality metals, enhance robustness and facilitate easier cleaning. This combination of lowered operating costs and enhanced reliability makes heat exchangers a wise investment, contributing to sustainable savings in both energy usage and maintenance costs.
Design and Care Guidelines
While designing heat exchangers, it is vital to factor in not just the expected thermal performance, but also additionally the practical aspects of installation and maintenance. A well-thought-out design can substantially lower potential downtime and increase operational efficiency. Elements such as serviceability for service, convenience of cleaning, and resource selection play a significant role. By including features that facilitate routine checks and maintenance, manufacturers can prolong the lifespan of heat exchangers and lessen the impact of fouling or other problems that may arise during operation.
Regular maintenance is vital to make certain that heat exchangers operate at peak efficiency. This comprises routine inspections to spot early signs of wear or fouling, which can affect performance and lead to escalating energy costs. Scheduled cleaning, together with monitoring systems that can pick up irregularities in temperature and pressure, allows for swift corrective actions. Moreover, comprehending the particular environmental conditions in which a heat exchanger operates can assist in developing targeted maintenance strategies that guarantee reliability and efficiency over time.
The selection of materials also notably impacts both the design and long-term maintenance of heat exchangers. Materials such as stainless steel are favored due to their corrosion resistance and strength, making them suitable for diverse applications, including those in the food and beverage and chemical industries. Innovations in compact heat exchanger design, along with advancements in digital monitoring technologies, further boost the ability to maintain maximum performance and extend the operational life of these critical components in diverse industrial applications.
