In the realm of engineering and energy efficiency, thermal exchangers stand out as critical devices that enable the transfer of thermal energy among several liquids. Their function to control heat effectively plays a vital role in multiple industries, including climate control systems that create suitable atmospheres to electricity-producing plants that create electricity. Comprehending how these devices operate, their different kinds, and their applications can offer valuable insights into their importance in today’s society.
As we explore the field of thermal exchange technology, we will examine their nature and how they function. We will compare the popular models such as shell & tube compared to plate heat exchangers, talk about their role in boosting energy efficiency, and highlight their importance in sectors such as chemical processing and clean energy. Additionally, we will examine maintenance practices frequent obstacles, and futuristic trends that are shaping the progress of heat exchanger technology, ensuring that you are ready with expertise for any endeavor or implementation involving these essential devices.
Understanding Thermal Exchangers
Thermal exchangers are essential devices used to transmit heat between multiple or more fluids at diverse temperatures without intermingling them. They play a key role in various industries by enhancing energy efficiency and preserving optimal operating conditions. By enabling the movement of heat, these systems help regulate temperature, assist manufacturing processes, and enhance the overall efficacy of thermal management in different applications.
There are several types of heat exchangers, each tailored for unique applications and working environments. Common types include shell and tube heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers, finned tube heat exchangers, and air-cooled heat exchangers. The selection of design often is influenced on aspects such as space availability, required heat transfer efficiency, and fluid characteristics. Comprehending the operational principles of these designs is important for picking the right heat exchanger for a given task.
In addition to different designs, particular materials are utilized for heat exchanger construction, influencing their durability and performance. Stainless steel is a frequent choice due to its corrosion resistance and strength. Additionally, the maintenance and troubleshooting of heat exchangers are important for staving off fouling and ensuring long-term performance. By comprehending the fundamentals of heat exchangers, one can recognize their importance across various applications, including HVAC, food processing, and energy generation.
Uses and Efficiency
Heat exchange devices play a crucial role in various commercial applications, enhancing efficiency and ensuring maximum performance across diverse sectors. In the chemicals industry, for instance, heat exchangers facilitate the movement of heat during processes and activities, significantly boosting energy utilization. In the food & drink industry, they are necessary for maintaining product quality during pasteurization and cooling processes, ensuring that temp regulation is consistently met for security and quality retention.
Efficiency is a significant advantage of utilizing heat exchangers. They permit for the repurposing of waste heat energy, which can drastically reduce operational costs. This is particularly clear in power plants, where heat exchangers improve thermal efficiency by moving heat from hot gases to a fluid, which can then be used to generate additional power. Furthermore, in HVAC systems, heat exchangers help in optimizing energy usage by recovering heating or cooling energy, leading to significant savings on energy bills.
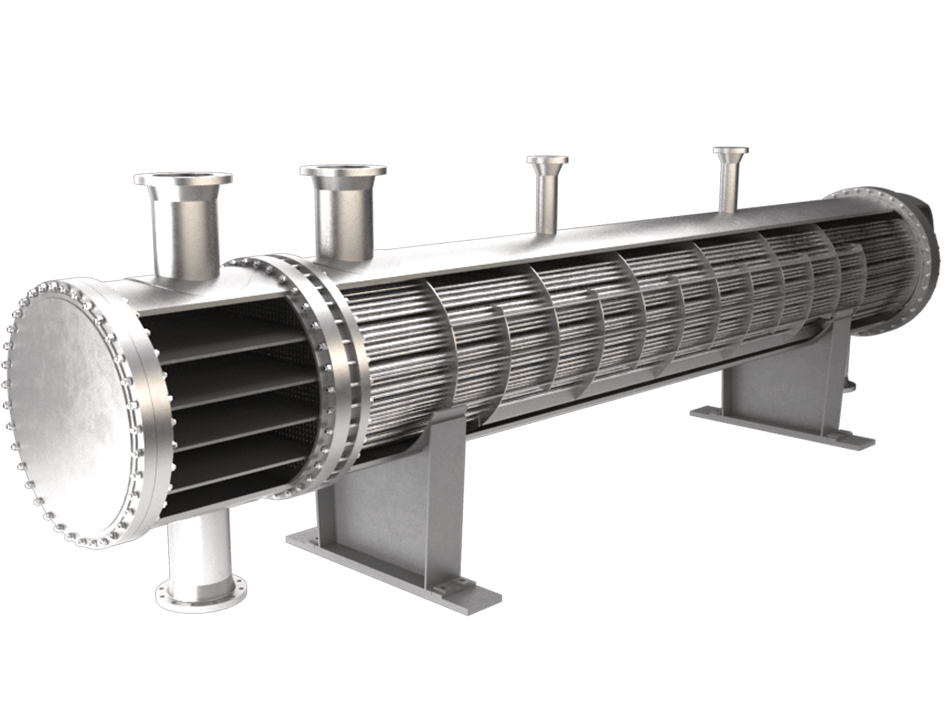
As energy efficiency becomes increasingly vital in contemporary engineering, innovations in heat exchanger design and materials are paving the way for improvements in sustainability. With Go here of space-saving and high-performance designs, such as plate heat exchangers, industries are finding that they can conserve space while boosting thermal performance. The trend toward using advanced materials, including stainless steel, also improves durability and resistance to corrosion, further prolonging the functionality and efficiency of these critical components.
Upkeep and Issues
Adequate maintenance of heat exchangers is essential to guarantee their effective operation and long lifespan. Routine inspections can help identify potential issues like scaling, corrosion, and leaks before they grow into major failures. Scheduled cleaning, whether through acidic descaling or mechanical methods, is essential to preserving heat transfer efficiency. Additionally, monitoring system pressures and temperatures helps in timely detection of anomalies that may indicate underlying problems.
One of the frequent challenges faced in heat exchanger maintenance is fouling, which happens when unwanted materials accumulate on heat transfer surfaces. This buildup can significantly diminish efficiency by hampering heat transfer and increasing operational costs. Implementing pre-treatment systems for process fluids and utilizing routine cleaning schedules can mitigate fouling risks. Comprehending the specific fouling characteristics of the fluids participating in the heat exchange process is key to developing effective maintenance strategies.
Another challenge is the selection of the appropriate materials for heat exchangers, particularly when dealing with corrosive fluids or extreme temperatures. Stainless steel is favored for its durability, but alternatives like titanium or custom alloys may be necessary for specific applications. Regular assessments of material integrity and the application of corrosion-resistant coatings can lengthen the service life of heat exchangers. Staying abreast of innovations in heat exchanger design and materials will assist in addressing these maintenance challenges effectively.
